

Proprietary technology and end-to-end services, supercharged by deep, long-term relationships

Lummus is the rare technology provider with expertise across the entire value chain, from diverse feedstock processing, heaters, catalysts, and digitalization to the end product.

With long-time customers and strategic technology partners, our unique ecosystem is built to fast-track technology development and commercialization.
On a solid foundation of expertise, we’ve built an infrastructure of forward technology, reinforced by continuous R&D, and magnified by our global networks.
Start with more than 160 technologies, everything from ethylene production to waste products recycling, water purification to renewable fuels. Add a unique ecosystem of global partners and customers, rowing in one direction to fast-track commercialization. And support all that bold thinking with continuous R&D.
Unlike any other company, Lummus connects every dot on the value chain to realize tomorrow’s ideas a day early.


We see a world in which operational excellence drives industry transformation. It’s a vision made real by leveraging our proprietary technologies and digital tools. Like our Short Residence Time (SRT®) pyrolysis heater, which maximizes feedstock efficiency while reducing costs.
Integrating AI allows us to further improve production and safety, delivering higher outputs with lower operating expenses, translating to a distinct competitive advantage.


With a range of integrated and energy-efficient solutions, we help our customers minimize waste, reduce carbon emissions, and achieve sustainable goals. We constantly advance technologies that destroy forever chemicals, improve wastewater treatment, electrify operations, recycle plastic waste, use renewable feedstocks, and more. Leading the energy transition, we're making the business case for sustainability.
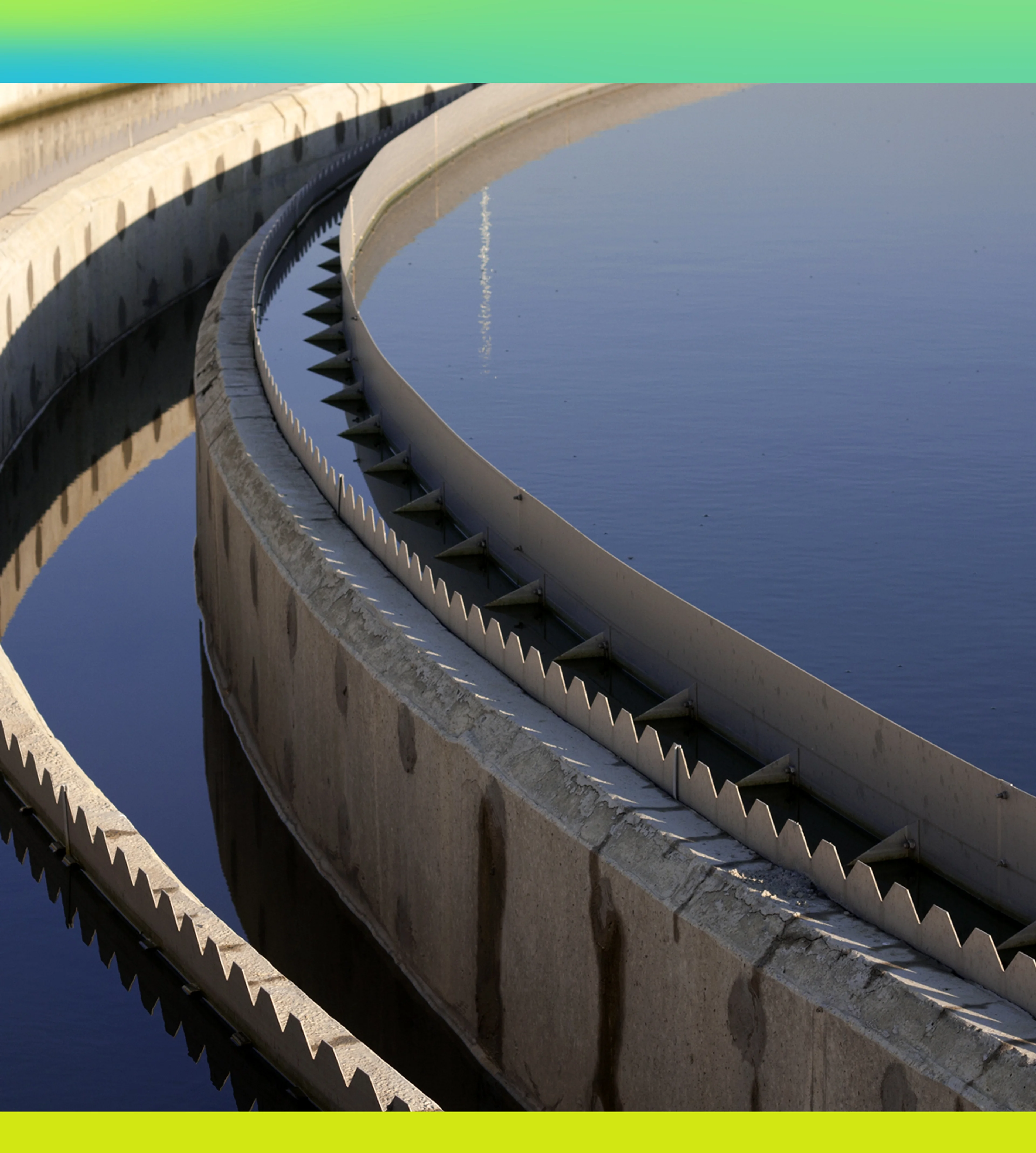


At Lummus, we strive to be a force for forward progress, giving big ideas ample runway for success through compelling ROI.
With decades of proprietary IP, expertise in catalyst and co-processing technology, robust and ongoing R&D, and a vast network of strategic partners and global customers, Lummus effects transformative growth, remaining agile enough to seize new opportunities in a rapidly changing marketplace.


Our unmatched IP portfolio is tailor-made for business growth. Not only that, we have an established track record for rapid commercialization next-generation technology.
From diverse raw feedstock processing to end products, we’re the rare tech provider connecting every link on the value chain, which positions us to quickly capitalize on emerging trends and capture markets for our customers and partners.


Our relationships tend to endure, and for good reason. Lummus leverages a world of expertise for collective success, creating an infrastructure for collaborative innovation and sustainable growth across a range of industries.
Shared expertise means greater reach. With 200+ partners and 1,000+ customers globally, we are uniquely positioned to realize what we envision. A world that works better, with lasting economic viability.

Success requires proven expertise, proactive curiosity, an instinct for commercialization, and the stamina to stay ahead of the curve. Lummus brings the complementary firepower to polymerization, plastics recycling, power generation, gas processing, water treatment, and other initiatives.


With analytics-fueled, AI-empowered insights applied across the downstream energy value chain, Lummus transforms your operations. We’ll help you implement and optimize to enhance monitoring, maintenance, troubleshooting, and safety, along with profits.


Our track record has earned us the trust of our clients, including project developers, buyers, and lenders. With global consulting services, we can provide an end-to-end blueprint for mitigating risk, driving growth, and solving business and operational challenges.

Lummus conducts complex feasibility studies, technical and economic analyses, licensor evaluations, and detailed cost estimates for implementing developing technologies for process plants worldwide, including multi-national refiners and petrochemical producers.


With a range of lifecycle services, Lummus can improve the efficiency and longevity of your processes. Support includes customized training programs, system and equipment reviews, solution implementation, maintenance forecasting, and more. For existing aftermarket services customers, please log in to the portal to access your dashboard.

Let’s transform tomorrow.
For solutions, support, and inspiration, Lummus can show you the way. It starts with a conversation. So, let’s have one.
